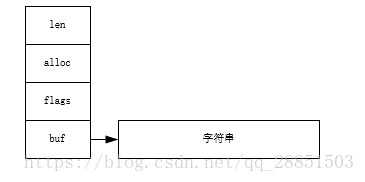
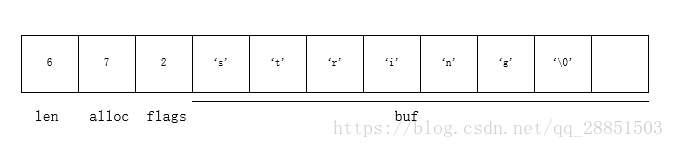
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| //sds最大空间预分配值(在头文件中顶定义)
#define SDS_MAX_PREALLOC (1024*1024)
/* Enlarge the free space at the end of the sds string so that the caller
* is sure that after calling this function can overwrite up to addlen
* bytes after the end of the string, plus one more byte for nul term.
*
* Note: this does not change the *length* of the sds string as returned
* by sdslen(), but only the free buffer space we have. */
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {
void *sh, *newsh;
size_t avail = sdsavail(s);
size_t len, newlen;
char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;
int hdrlen;
/* Return ASAP if there is enough space left. */
if (avail >= addlen) return s;
//如果可用空间不足的情况下,进行空间增加
len = sdslen(s);
sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
newlen = (len+addlen);
if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)
//小于1M直接变为原来的2倍
newlen *= 2;
else
//大于1M的情况,累加1M
newlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;
type = sdsReqType(newlen);
/* Don't use type 5: the user is appending to the string and type 5 is
* not able to remember empty space, so sdsMakeRoomFor() must be called
* at every appending operation. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
if (oldtype==type) {
newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
} else {
/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,
* and can't use realloc */
newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);
s_free(sh);
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
s[-1] = type;
sdssetlen(s, len);
}
sdssetalloc(s, newlen);
return s;
}
/* Reallocate the sds string so that it has no free space at the end. The
* contained string remains not altered, but next concatenation operations
* will require a reallocation.
*
* After the call, the passed sds string is no longer valid and all the
* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call. */
sds sdsRemoveFreeSpace(sds s) {
void *sh, *newsh;
char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;
int hdrlen, oldhdrlen = sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
size_t len = sdslen(s);
sh = (char*)s-oldhdrlen;
/* Check what would be the minimum SDS header that is just good enough to
* fit this string. */
type = sdsReqType(len);
hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
/* If the type is the same, or at least a large enough type is still
* required, we just realloc(), letting the allocator to do the copy
* only if really needed. Otherwise if the change is huge, we manually
* reallocate the string to use the different header type. */
if (oldtype==type || type > SDS_TYPE_8) {
newsh = s_realloc(sh, oldhdrlen+len+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)newsh+oldhdrlen;
} else {
newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+len+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);
s_free(sh);
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
s[-1] = type;
sdssetlen(s, len);
}
sdssetalloc(s, len);
return s;
}
|